JOBS IN PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS
JOBS IN PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS
There Are Two Types Of Banks In Any Country
One is the Central Bank which implements the monetary policy of the Government and acts as the “Bankers Bank”. The others are commercial banks which pro- vide banking services to its customers. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of the country. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was set up on the basis of the recommendations of the Hilton Young Commission. The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (II of 1934) provides the statutory basis of the functioning of the Bank, which commenced operations on April 1, 1935. Unlike other banks, RBI does not provide banking services to the customers. But, it regulates the monetary policy of the country. It also provides banking services to the bank. Seniority levels of RBI Officers are divided into Groups (A to F). Group ‘A’ is junior-most while Group ‘F’ is the senior- most level like Deputy-Governor, Governor. All these officers collectively are called as Class-I employees. Apart from these employees RBI also has a large number of Class-III and Class-IV employees who work as service staff and other subordinate levels. There is no Class-II level in RBI. Every year, direct recruitment of Officers is carried out at Group ‘A’ & ‘B’ levels and at Group ‘C’ & ‘D’ levels for experienced people. While Group ‘A’, ‘C’ & ‘D’ recruitment is nominal, there are frequent recruitments of college graduates and postgraduates for Group ‘B’ level through examinations conducted by Reserve Bank of India Services Board (RBISB).

A. RESERVE BANK OF INDIA SERVICES BOARD (WWW.RBI.GOV.IN).
The RBISB issues notifications from time to time for the recruitment of following ten posts:
1.Research Officer in Grade B for Department of Economic
and Policy Research
2.Research Officer in Grade B for the Department of
Statistics and Information Management
3.Officer in Grade B DR General
4.Manager (Technical-Civil) in Grade B
5.Manager (Technical-Electrical) in Grade B
6.Assistant Manager (Technical-Electrical) in Grade A
7.Assistant Manager (Technical-Civil) in Grade A
8.Assistant Manager (Security) in Grade A
9.Assistant Manager (Rajbhasha) in Grade A
10.Assistants (Clerk)
The most common of them is the recruitment for Grade B Officers. Graduates between the age of 21 to 30 years are eligible to apply.
Scheme of Selection for Grade B Officers:
•Selection is done through Examinations and Interview.
•Examinations are held in two phases :
(I) Phase-I Online Examination (Objective Type):
This paper approximately of 3 hours duration for 200 marks. The paper consists of
following tests:
• General Awareness
• English Language
• Quantitative Aptitude and
• Reasoning/Mental Ability/Aptitude
(II) Phase-II Written Examination (Descriptive Type):
The Phase-II written examination (WE) is conducted only for those candidates who are shortlisted for the same. The examination consists of three Descriptive Type papers —
• Paper I — English
• Paper II — Economic and Social Issues and
• Paper III — Finance and Management
Each of these papers is for 3 hours duration carrying 100 marks. For the details of pattern of examination of other posts recruited in the RBI, it is advised to refer the notification published on the website www.rbi.org.
B. STATE BANK OF INDIA AND ITS ASSOCIATE BANKS
State Bank of India (SBI) is the largest commercial bank in India in terms of assets, deposits, profits, branches, customers and employees. The Government of India is the single largest shareholder of this Fortune 500 entity with 61.58% ownership. The origins of State Bank of India date back to 1806 when the Bank of Calcutta (later called the Bank of Bengal) was established. In 1921, the Bank of Bengal and two other banks (Bank of Madras and Bank of Bombay) were amalgamated to form the Imperial Bank of India. In 1955, the Reserve Bank of India acquired the controlling interests of the Imperial Bank of India and SBI was created by an act of Parliament to succeed the Imperial Bank of India. Recruitment for SBI as well as the five Associate banks of SBI is done by the Central Recruitment and Promotion Department of the SBI located at Mumbai. The five Associate Banks of SBI are:- (1) SBBJ : State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur (2) SBH : State Bank of Hyderabad (3) SBM : State Bank of Mysore (4) SBP : State Bank of Patiala (5) SBT : State Bank of Travancore From time to time State Bank of India issues notification for the recruitment of Probationary Officers and Clerks.
1. Syllabus for Probationary Officers Exam Paper I - Objective type - 200 Marks
• English Language
• Reasoning
• General Awareness
• Data analysis and interpretation
Paper II - Descriptive Section - 50 Marks
Letter Writing, Paragraph Writing, Essay Writing, Precise Writing, Reading Comprehension Interview 2. SBI Clerk Examination 10 + 2 passed candidates from 18 to 26 years can apply for the post. Each section contains objective-type questions for 40 marks. So the total marks for Clerk exam is 200. There is negative marking for each wrong answer. It is always better to prepare intensively and at- tempt limited questions with correct answer to get a call for next round i.e. Interview.
• General Awareness
• Quantitative Aptitude
• Reasoning Ability
• General English language
• Computer knowledge/marketing aptitude
Recruitment for other Public Sector Banks
Public sector banks are banks where the majority stakes are held by the Government and the shares are listed on the stock exchange. There are about 79 scheduled commercial banks out of which 26 are public sector banks. RBI is expected to issue more banking li- censes to private sector players by 2015. The following are the list of public sector banks:
1.Allahabad Bank (www.allahabadbank.in)
2.Andhra Bank (www.andhrabank.in)
3.Bank of Baroda (www.bankofbaroda.com)
4.Bank of India (www.bankofindia.com)
5.Bank of Maharashtra (www.bankofmaharashtra.in)
6.Canara Bank (www.canarabank.com)
7.Central Bank of India (www.centralbankofindia.co.in)
8.Corporation Bank (www.corpbank.com)
9.Dena Bank (www.denabank.com)
10.IDBI Bank Limited (www.idbi.com)
11.Indian Bank (www.indianbank.in)
12.Indian Overseas Bank (www.iob.in)
13.Oriental Bank of Commerce (www.obcindia.co.in)
14.Punjab & Sind Bank (www.psbindia.com)
15.Punjab National Bank (www.pnbindia.com)
16.State Bank of India (www.statebankofindia.com)
17.Syndicate Bank (www.syndicatebank.in)
18.UCO Bank (www.ucobank.com)
19.Union Bank of India (www.unionbankofindia.co.in)
20.United Bank of India (www.unitedbankofindia.com)
21.Vijaya Bank (www.vijayabank.com)
22.State Bank of Bikaner & Jaipur (www.sbbjbank.com)
23.State Bank of Hyderabad (www.sbhyd.com)
24.State Bank of Mysore (www.statebankofmysore.co.in)
25.State Bank of Patiala (www.sbp.co.in)
26.State Bank of Travancore (www.statebankoftravancore.com)
Public sector banks in India recruit at entry level through a selection process. The advertisements for recruitment are published in the newspapers as well as Employment News. The details of the no- tification can also be accessed on the website of the respective recruiting agency. The recruitment to Reserve Bank of India is done by Reserve Bank of India Services Board. State Bank of India and its associates conduct written test and interview separately for their recruitment of the clerical cadre and PO posts through the Central Recruitment and promotion department of SBI. Regional rural banks (RRBs) also conduct their recruitment through a test conducted by IBPS.
Recruitment for NABARD is being done by their respective services boards. A total of 19 public sector banks have come together to participate in the Common Written Exam (CWE) conducted by Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS). Banks use CWE scores to shortlist candidates for Clerical cadre, Probationary officers (PO) and Specialist officers. Shortlisted candidates are called for group discussion and personal interviews and the final selection is done on the basis of the combined scores of both the stages. Graduate in any stream can appear for these tests. The test is objective type with questions on reasoning, English language, numerical ability, general awareness and computer knowledge. Private sector banks have their own aptitude tests and interview process to recruit at the entry level. Most of the banks have their in- house training programs to up-skill the employees. These trainings can be supplemented with exams like JAIIB and CAIIB conducted by Indian Institute of Banking and Finance (IIBF). These objective type exams also help in career advancement from the officer level to the management level.
A. INSTITUTE OF BANKING PERSONNEL SELECTION (WWW.IBPS.IN)
Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS) is an autonomous agency in India, which started its operation in 1975 as Personnel Selection Services (PSS). In 1984, IBPS became an independent entity at the behest of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Public Sector Banks. IBPS is envisioned as a self-governed academic and research oriented institute, with a mission of enhancing human- resource development through personnel assessment. In 2011, IBPS announced a common written examination (CWE) for the selection Officers and Clerks in Indian banks. IBPS CWE is now mandatory for anyone who seeks an employment in 20 public sector and Regional Rural banks except State Bank of India and its Associate Banks. IBPS periodically accepts the exam applications from the candidates at their website www.ibps.in, and the exams are orga- nized at various locations in the country either in online or offline mode. The Governing Board consists of nominees from Reserve Bank of India, Ministry of Finance Government of India, National Institute of Bank Management, representatives of Public Sector Banks, Insurance sector and academics. The matters related to policy and affairs of the Institute are vested in the Governing Board. The other representatives are from Allahabad Bank, Andhra Bank, Bank of Baroda, Bank of India, Bank of Maharashtra, Bharatiya Mahila Bank, Canara Bank, Central Bank of India, Corporation Bank, Dena Bank, Indian Bank, Indian Overseas Bank, Oriental Bank of Commerce, Punjab National Bank, Punjab & Sind Bank, Syndicate Bank, Union Bank of India, United Bank of India, UCO Bank, Vijaya Bank, IDBI Bank and Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India Bank. IBPS also does recruitment for the Regional Rural Banks through a separate exam. IBPS conducts the following examinations
1.Common Written Exam (CWE) for Probationary Officers/ Management Trainee
This is a common exam for the recruitment for the post of Probationary Officers/ Management Trainees in the participant member Banks. The successful candidates are initially posted as Probationary Officer or
Management Trainee and can reach to higher management ranks on the basis of their performance.
2.Common Written Exam (CWE) for Specialist Officers
There are several posts like IT Officer, Agricultural Field Officer, Rajbhasha Adhikari, Law Officer, Human Re- source/Per-son- Officer etc in banks. The recruitment to these posts is done through a separate exam conducted by IBPS for the participant banks.
3.Common Written Exam (CWE) for Clerks
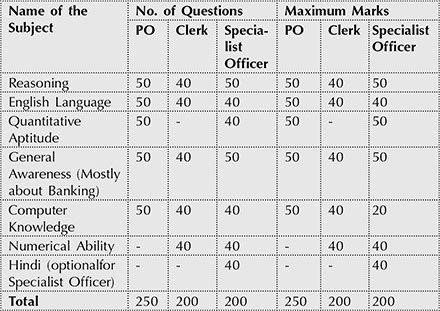
The clerical posts in banks are filled through a separate exam con- ducted by IBPS for its participant banks. Exam pattern and marks distribution for IBPS exams are listed below:
B. NATIONAL BANK FOR AGRICULTURE AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT (NABARD)
NABARD was set up in 1982 as an apex development bank to focus on facilitating credit flow for the promotion of agriculture, small scale industries, cottage & village industries, handicrafts and other rural crafts. The recruitment for the NABARD is done by NABARD Services Board through special recruitment notification as per the vacancy available. It conducts entrance tests for the post of:
1.Manager Grade B
2.Assistant Manager Grade A
3.Clerk
C. CO-OPERATIVE BANKS
Co-operative banks have been formed to provide financial services to the members of the bank itself who are owners as well as customers. The aim is not to maximize profits but to provide banking services, loans etc. to the members. The co-operative banking structure in India is divided into following main categories:
1. Primary Urban Co-op Banks/Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
The Primary Co-operative Credit Society is an association of borrowers and non-borrowers residing in a particular locality. The funds of the society are derived from the share capital and deposits of members and loans from central co-operative banks. The borrowing powers of the members as well as of the society are fixed. The loans are given to members for the purchase of cattle, fodder, fertilizers, pesticides, implements, etc.
3.State Co-operative Banks
The state co-operative bank is a federation of central co- operative bank and acts as a watchdog of the co-operative banking structure in the state. Its funds are obtained from share capital, deposits, loans and overdrafts from the Re- serve Bank of India. The state co-operative banks lend money to central co-operative banks and primary societies and not directly to farmers.
3.State Co-operativ Banks
The land development banks are organized in three tiers viz. state, central and primary level and they meet the long term credit requirements of the farmers for developmental purposes. The state land development bank oversees the primary land development banks situated in the districts and tehsils in the state. They are governed both by the state government and Reserve Bank of India. Recently, the supervision of land development banks has been assumed by National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD). The sources of funds for these banks are the debentures subscribed by both central and state government. These banks do not accept deposits from the general public.
Co-operative banks also issue vacancy notifications for the recruitment under various cadres like Manager, Assistant Manager, Clerks etc. There is no centralized procedure for recruitment and different banks conduct their own examination. Some co-operative banks also conduct recruitment through IBPS.
Note: Candidates are advised to visit the website of the respective recruit- ing organizations to access the details of the eligibility and the pat- tern of examinations.
You may also like
PUBLIC SECTOR INSURANCE COMPANY
PUBLIC SECTOR INSURANCE COMPANY Though the Public Sector Insurance Companies are Central PSUs, these companies are dealt separately to give adequate focus to job opportunities available in this promising and emerging sector of the Indian economy. There is no substitute …
GOVERNMENT JOBS HIMACHAL PRADESH
GOVERNMENT JOBS HIMACHAL PRADESH The recruitment to various services in the state is done by Himachal Pradesh Public Service Commission (HPPSC). There are following types of entrance tests Recruitment through examination followed by viva-voce: Through this method of recruitment the …
JOBS IN PUBLIC SECTOR UNDERTAKING
JOBS IN PUBLIC SECTOR UNDERTAKING The Central PSUs or enterprises are categorized into Maharatna, Navratna, Miniratna companies based on gross turnover, profitability and certain other performance parameters. Some of the Central and States companies are listed on the Mumbai and …
